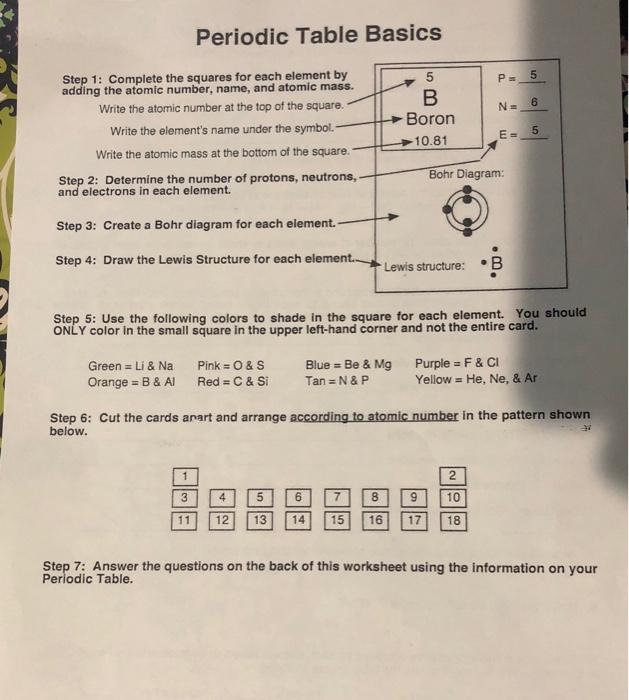


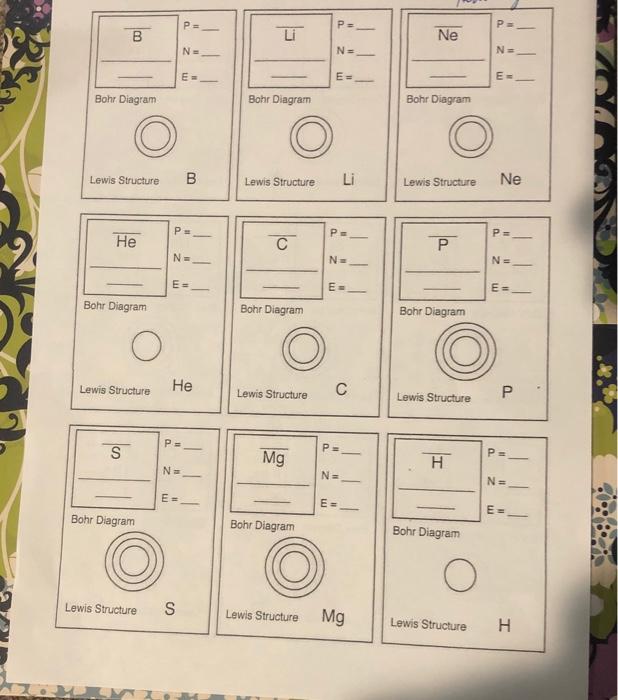
 Regular dining table fundamentals P 5 NE 6 5 B Boron 10.81 1: finish the squares for every single element with the addition of the atomic quantity, title, and atomic mass. Write the atomic quantity near the top of the square. Write the element’s title in expression. Write the atomic mass in the bottom regarding the square. Step two: Determine the amount of protons, neutrons, and electrons in each element. E = 5 Bohr Diagram: 3: Make a Bohr diagram for every single element. Step four: Draw the Lewis construction for every single element.. Lewis framework: B Action 5: utilize the following colors to shade within the square for every single element. You need to JUST color within the tiny square within the top left-hand part and never the whole card. Green = Li & Na Pink=&S Orange = B & Al Red = C & Si Blue = Be & Mg Tan=N&P Purple = F & CI Yellow = He, Ne, & Ar action 6: slice the cards arart and organize in accordance with atomic quantity within the pattern shown below. 2 3 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 action 7: respond to the concerns regarding the straight back of the worksheet utilizing the info on your regular dining table Periodic Table Basics 1. Which elements had complete outer shells? Supply the title and expression for every single. 2. just what can you notice concerning the located area of the elements in no. 1? 3. Which elements had just one valence electron? 4. just what can you notice concerning the located area of the elements in # 3? 5. just what can you notice concerning the wide range of valence electrons while you move from remaining to right across a row or duration within the regular dining table? (Na – Mg – Al – Si –PS-CI – Ar) 6. Exactly what can you notice concerning the wide range of stamina or shells while you move down an organization or line within the regular dining table? (H — Li – Na) 7. Elements are arranged into families in accordance with their real and chemical properties. Recognize the weather you found in action 5 that participate in each family members in line with the wide range of valence electrons. Supply the title and expression for every single element. Alkali Metals – 1 valence electron Alkaline world Metals – 2 valence electrons Boron Family – 3 valence electrons & Carbon Family – 4 valence electrons Nitrogen Family – 5 valence electrons & Oxygen Family – 6 valence electrons Halides – 7 valence electrons Noble Gases – Complete outermost shell & 8. just what can you notice concerning the located area of the elements in each family members? 9. just how can you classify hydrogen? Why? 10. Anticipate the amount of valence electrons for every single element according to its location within the regular dining table of Elements. You will have to utilize the dining table inside textbook. Barium = Lead = Xenon = Potassium = P P. N ΑΙ F N= N= N- E = E- E= Bohr Diagram Bohr Diagram Bohr Diagram Lewis construction N AI TI Lewis construction Lewis construction Ps P = P= Ar Si Na N. NE N= m E- E- Bohr Diagram Bohr Diagram Bohr Diagram Lewis construction Ar Lewis construction Si Lewis construction Na P PE PE Be o CI N. N= NE E= E= E = Bohr Diagram Bohr Diagram Bohr Diagram Lewis construction become Lewis construction o Lewis construction СІ PE P= P B Ne NE N- N. E- E= E Bohr Diagram Bohr Diagram Bohr Diagram Lewis construction B Lewis construction Li Lewis construction Ne P. PE P= He с Р N N= NE E E- E Bohr Diagram Bohr Diagram Bohr Diagram Lewis construction He Lewis construction C Lewis construction Р P. S P PE Mg H N. NE NE EE E E- Bohr Diagram Bohr Diagram Bohr Diagram Lewis construction S Lewis construction Mg Lewis construction H
Regular dining table fundamentals P 5 NE 6 5 B Boron 10.81 1: finish the squares for every single element with the addition of the atomic quantity, title, and atomic mass. Write the atomic quantity near the top of the square. Write the element’s title in expression. Write the atomic mass in the bottom regarding the square. Step two: Determine the amount of protons, neutrons, and electrons in each element. E = 5 Bohr Diagram: 3: Make a Bohr diagram for every single element. Step four: Draw the Lewis construction for every single element.. Lewis framework: B Action 5: utilize the following colors to shade within the square for every single element. You need to JUST color within the tiny square within the top left-hand part and never the whole card. Green = Li & Na Pink=&S Orange = B & Al Red = C & Si Blue = Be & Mg Tan=N&P Purple = F & CI Yellow = He, Ne, & Ar action 6: slice the cards arart and organize in accordance with atomic quantity within the pattern shown below. 2 3 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 action 7: respond to the concerns regarding the straight back of the worksheet utilizing the info on your regular dining table Periodic Table Basics 1. Which elements had complete outer shells? Supply the title and expression for every single. 2. just what can you notice concerning the located area of the elements in no. 1? 3. Which elements had just one valence electron? 4. just what can you notice concerning the located area of the elements in # 3? 5. just what can you notice concerning the wide range of valence electrons while you move from remaining to right across a row or duration within the regular dining table? (Na – Mg – Al – Si –PS-CI – Ar) 6. Exactly what can you notice concerning the wide range of stamina or shells while you move down an organization or line within the regular dining table? (H — Li – Na) 7. Elements are arranged into families in accordance with their real and chemical properties. Recognize the weather you found in action 5 that participate in each family members in line with the wide range of valence electrons. Supply the title and expression for every single element. Alkali Metals – 1 valence electron Alkaline world Metals – 2 valence electrons Boron Family – 3 valence electrons & Carbon Family – 4 valence electrons Nitrogen Family – 5 valence electrons & Oxygen Family – 6 valence electrons Halides – 7 valence electrons Noble Gases – Complete outermost shell & 8. just what can you notice concerning the located area of the elements in each family members? 9. just how can you classify hydrogen? Why? 10. Anticipate the amount of valence electrons for every single element according to its location within the regular dining table of Elements. You will have to utilize the dining table inside textbook. Barium = Lead = Xenon = Potassium = P P. N ΑΙ F N= N= N- E = E- E= Bohr Diagram Bohr Diagram Bohr Diagram Lewis construction N AI TI Lewis construction Lewis construction Ps P = P= Ar Si Na N. NE N= m E- E- Bohr Diagram Bohr Diagram Bohr Diagram Lewis construction Ar Lewis construction Si Lewis construction Na P PE PE Be o CI N. N= NE E= E= E = Bohr Diagram Bohr Diagram Bohr Diagram Lewis construction become Lewis construction o Lewis construction СІ PE P= P B Ne NE N- N. E- E= E Bohr Diagram Bohr Diagram Bohr Diagram Lewis construction B Lewis construction Li Lewis construction Ne P. PE P= He с Р N N= NE E E- E Bohr Diagram Bohr Diagram Bohr Diagram Lewis construction He Lewis construction C Lewis construction Р P. S P PE Mg H N. NE NE EE E E- Bohr Diagram Bohr Diagram Bohr Diagram Lewis construction S Lewis construction Mg Lewis construction H
1. helium He, neon Ne, argon Ar
2. they’ve been found in the final line in other words rightmost coulmn of
3. metals have actually just one electron in valence shell
4.they are observed in exact same line in other words in leftmost coulm regarding the
hydrogen, lithium, salt.
the regular dining table. called noble gases.
regular dining table and called alkali metals
This is the collective voice of the talented editorial team at Answerprime.com. Committed to delivering high-quality content, this account represents the collaborative efforts of knowledgeable experts. With a passion for research and a dedication to accuracy, Answerprime brings you insightful articles across various subjects. Explore a diverse range of expertise and perspectives curated by the editorial team through the lens of Answerprime.
Latest posts by Answer Prime
(see all)




